SCXML-tutorial
| Contents | Overview | Examples | Editor | Forum |
|---|
<send>
The element is used to send events and data to external systems, including external SCXML Interpreters, or to raise events in the current SCXML session.
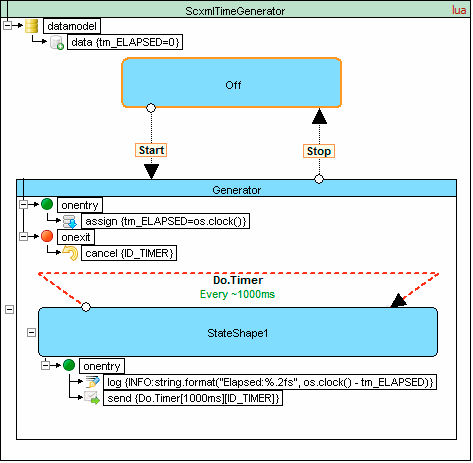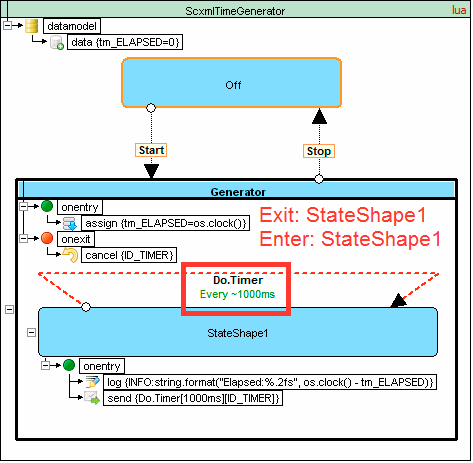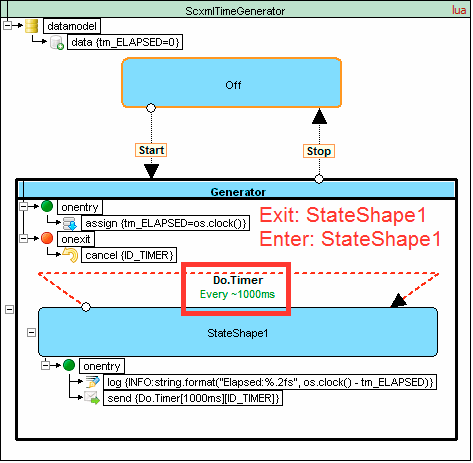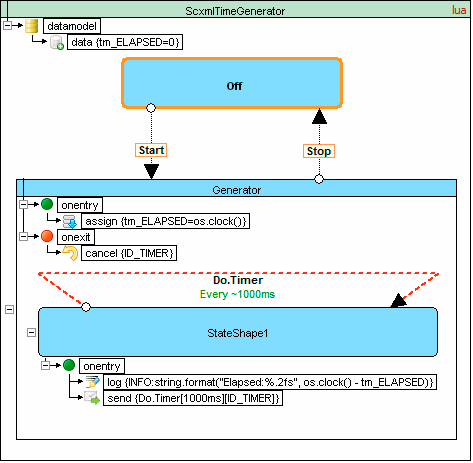
<scxml datamodel="lua" initial="Off" name="ScxmlTimeGenerator" version="1.0" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2005/07/scxml">
<datamodel>
<data expr="0" id="tm_ELAPSED"/>
</datamodel>
<state id="Off">
<transition event="Start" target="Generator"/>
</state>
<state id="Generator">
<onentry>
<assign expr="os.clock()" location="tm_ELAPSED"/>
</onentry>
<onexit>
<cancel sendid="ID_TIMER"/>
</onexit>
<transition event="Stop" target="Off"/>
<state id="StateShape1">
<onentry>
<log expr="string.format('Elapsed:%.2fs', os.clock() - tm_ELAPSED)" label="INFO"/>
<send delay="1000ms" event="Do.Timer" id="ID_TIMER"/>
</onentry>
<transition event="Do.Timer" target="StateShape1"/>
</state>
</state>
</scxml>
Attribute Details
1. 'event'
A string indicating the name of message being generated. Must not occur with 'eventexpr'. If the type is http://www.w3.org/TR/scxml/#SCXMLEventProcessor, either this attribute or 'eventexpr' must be present.
2. 'eventexpr'
A dynamic alternative to 'event'. If this attribute is present, the SCXML Processor must evaluate it when the parent <send> element is evaluated and treat the result as if it had been entered as the value of 'event'. Must not occur with 'event'. If the type is http://www.w3.org/TR/scxml/#SCXMLEventProcessor, either this attribute or 'event' must be present.
3. 'target'
The unique identifier of the message target that the platform should send the event to. See 6.2.4 The Target of Send for details. Must not occur with 'targetexpr'.
When using the SCXML Event I/O Processor, SCXML Processors must support the following special targets for <send>:
#_internal. The Processor must add the event to the internal event queue of the sending session.
<state id="Parent">
<invoke autoforward="true" id="ID_MODULE_CHILD" src="Child.scxml"/>
<onentry>
<!-- event 'Timeout' will not come to any invoked session -->
<send event="Timeout" target="#_internal"/>
</onentry>
</state>
#_scxml_sessionid. If the target is the special term #_scxml_sessionid (#_scxml_ + sessionid), where sessionid is the id of an SCXML session that is accessible to the Processor, the Processor must add the event to the external queue of that session. The set of SCXML sessions that are accessible to a given SCXML Processor is platform-dependent.
<state id="Parent">
<transition event="Msg.From.Child">
<send delay="1s" event="Quit.Child" targetexpr="'#_scxml_' + _event.data"/>
</transition>
</state>
#_parent. The Processor must add the event to the external event queue of the SCXML session that invoked the sending session, if there is one. See <invoke> for details.
<state id="Child">
<onentry>
<send event="Msg.From.Child" target="#_parent">
<content expr="_sessionid"/>
</send>
</onentry>
</state>
#_invokeid. If the target is the special term #_invokeid (#_ + invokeid), where invokeid is the invokeid of an SCXML session that the sending session has created by <invoke>, the Processor must add the event to the external queue of that session. See <invoke> for details.
<state id="Parent">
<invoke id="ID_MODULE_CHILD" src="Child.scxml" autoforward="false" />
<onentry>
<!-- invoked session with id 'ID_MODULE_CHILD' will receive event 'Timeout' after 2 seconds -->
<send delay="2s" event="Timeout" target="#_ID_MODULE_CHILD"/>
</onentry>
</state>
Example showing usage of #_parent and #_scxml_
Parent machine invokes child machine that sends event to parent. Event contains event origin which is equialent #_scxml_ + sessionid and parent machine uses it to respond
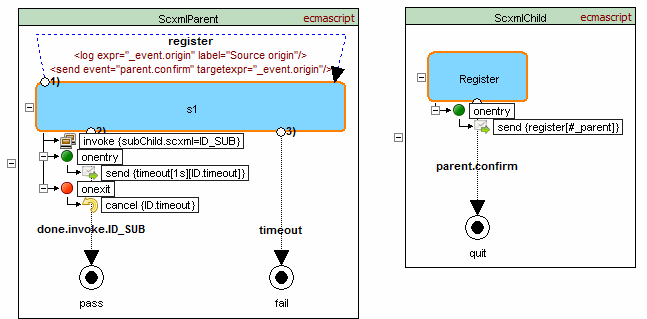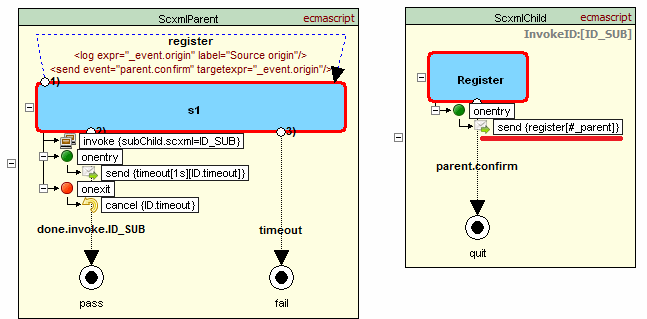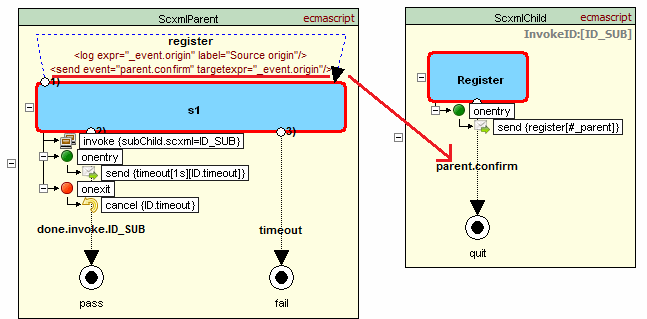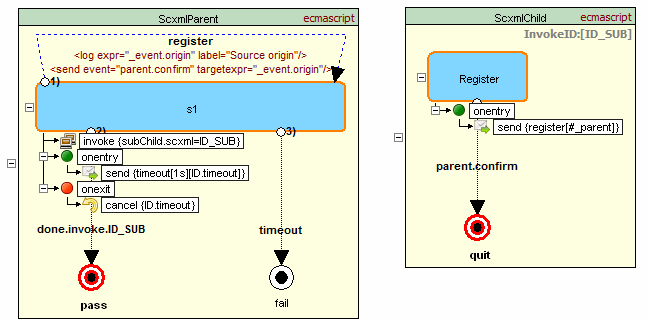
Source code - parent
<scxml datamodel="ecmascript" initial="s1" name="ScxmlParent" version="1.0" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2005/07/scxml">
<state id="s1">
<invoke id="ID_SUB" src="subChild.scxml"/>
<onentry>
<send delay="1s" event="timeout" id="ID.timeout"/>
</onentry>
<onexit>
<cancel sendid="ID.timeout"/>
</onexit>
<transition event="register">
<log expr="_event.origin" label="Source origin"/>
<send event="parent.confirm" targetexpr="_event.origin"/>
</transition>
<transition event="done.invoke.ID_SUB" target="pass"/>
<transition event="timeout" target="fail"/>
</state>
<final id="pass"/>
<final id="fail"/>
</scxml>
Source code - child
<scxml datamodel="ecmascript" initial="Register" name="ScxmlChild" version="1.0" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2005/07/scxml">
<state id="Register">
<onentry>
<send event="register" target="#_parent"/>
</onentry>
<transition event="parent.confirm" target="quit"/>
</state>
<final id="quit"/>
</scxml>
4. 'targetexpr'
A dynamic alternative to 'target'. If this attribute is present, the SCXML Processor must evaluate it when the parent <send> element is evaluated and treat the result as if it had been entered as the value of 'target'. Must not occur with 'target'.
5. 'type'
The URI that identifies the transport mechanism for the message. See 6.2.5 The Type of Send for details. Must not occur with 'typeexpr'.
5.1. SCXML Event I/O Processor (Default).
Target is an SCXML session. The transport mechanism is platform-specific.
<send delay="2s" event="Timer"/>
<send delay="2s" event="Timer" type="http://www.w3.org/TR/scxml/#SCXMLEventProcessor"/>
5.2. Basic HTTP Event I/O Processor
Target is a URL. Data is sent via HTTP POST
<send event="ToRemoteMachine" type="http://www.w3.org/TR/scxml/#BasicHTTPEventProcessor"/>
6. 'typeexpr'
A dynamic alternative to 'type'. If this attribute is present, the SCXML Processor must evaluate it when the parent <send> element is evaluated and treat the result as if it had been entered as the value of 'type'. Must not occur with 'type'.
7. 'id'
A string literal to be used as the identifier for this instance of <send>. See 3.14 IDs for details. Must not occur with 'idlocation'.
<state id="start">
<onentry>
<send delay="5s" event="Timer2" id="ID_Timer2"/>
</onentry>
<onexit>
<cancel sendid="ID_Timer2"/>
</onexit>
</state>
8. 'idlocation'
Any location expression evaluating to a data model location in which a system-generated id can be stored. Must not occur with 'id'.
9. 'delay'
A time designation as defined in CSS2 format. Indicates how long the processor should wait before dispatching the message. Must not occur with 'delayexpr' or when the attribute 'target' has the value #_internal.
<send delay="4s" event="Timer1"/>
<send delay="500ms" event="Timer2"/>
10. 'delayexpr'
A value expression which returns a time designation as defined in CSS2 format. A dynamic alternative to 'delay'. If this attribute is present, the SCXML Processor must evaluate it when the parent <send> element is evaluated and treat the result as if it had been entered as the value of 'delay'. Must not occur with 'delayexpr' or when the attribute 'target' has the value #_internal.
<send delayexpr="2*2 + 's'" event="Timer1"/>
<send delay="5*100 + 'ms'" event="Timer2"/>
11. 'namelist'
List of valid location expressions. A space-separated list of one or more data model locations to be included as attribute/value pairs with the message. (The name of the location is the attribute and the value stored at the location is the value.) See 5.9.2 Location Expressions for details.
W3C IRP tests
1. Test 172
If 'eventexpr' is present, the SCXML Processor MUST evaluate it when the parent <send> element is evaluated and treat the result as if it had been entered as the value of 'event'.

2. Test 173
If 'targetexpr' is present, the SCXML Processor MUST evaluate it when the parent <send> element is evaluated and treat the result as if it had been entered as the value of 'target'.

3. Test 174
If 'typexpr' is present, the SCXML Processor MUST evaluate it when the parent <send> element is evaluated and treat the result as if it had been entered as the value of 'type'.

4. Test 175
If 'delayexpr' is present, the SCXML Processor MUST evaluate it when the parent <send> element is evaluated and treat the result as if it had been entered as the value of 'delay'.

5. Test 176
The SCXML Processor MUST evaluate param when the parent <send> element is evaluated and pass the resulting data unmodified to the external service when the message is delivered.

6. Test 178
The SCXML Processor MUST include all attributes and values provided by param and/or 'namelist' even if duplicates occur.

<scxml datamodel="lua" initial="s0" name="Scxml_Test178" version="1.0" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2005/07/scxml">
<state id="s0">
<onentry>
<send event="event1">
<param expr="2" name="Var1"/>
<param expr="3" name="Var1"/>
</send>
</onentry>
<transition event="event1" target="final">
<log label="_event " expr="_event"/>
</transition>
<transition event="*" target="fail"/>
</state>
<final id="final"/>
<final id="fail">
<onentry>
<log expr="'fail'" label="Outcome"/>
</onentry>
</final>
</scxml>
Output:
External Event: event1, interpreter [Scxml_Test178]
[Log] _event : {
"data": {
"Var1": 3
},
"name": "event1",
"origin": "#_scxml_7927b337-addb-4eb5-bcf6-f12e42828924",
"origintype": "http://www.w3.org/TR/scxml/#SCXMLEventProcessor",
"type": "external"
}
7. Test 179
The SCXML Processor MUST evaluate the <content> element when the parent <send> element is evaluated and pass the resulting data unmodified to the external service when the message is delivered.

8. Test 183
If 'idlocation' is present, the SCXML Processor MUST generate an id when the parent <send> element is evaluated and store it in this location.

9. Test 185
If a delay is specified via 'delay' or 'delayexpr', the SCXML Processor MUST interpret the character string as a time interval. the SCXML Processor MUST dispatch the message only when the delay interval elapses.

10. Test 186
The Processor MUST evaluate all arguments to send when the send element is evaluated, and not when the message is actually dispatched.

11. Test 187
If the SCXML session terminates before the delay interval has elapsed, the SCXML Processor MUST discard the message without attempting to deliver it.


12. Test 194
If the value of the 'target' or 'targetexpr' attribute is not supported or invalid, the Processor MUST place the error error.execution on the internal event queue.

13. Test 198
If neither the 'type' nor the 'typeexpr' is defined, the SCXML Processor MUST assume the default value of http://www.w3.org/TR/scxml/#SCXMLEventProcessor.

14. Test 199
If the SCXML Processor does not support the type that is specified, it MUST place the event error.execution on the internal event queue.

15. Test 200
SCXML Processors MUST support the type http://www.w3.org/TR/scxml/#SCXMLEventProcessor.

16. Test 201
Processors that support HTTP POST must use the value http://www.w3.org/TR/scxml/#BasicHTTPEventProcessor for the 'type' attribute.

The sending SCXML Interpreter MUST not alter the content of the send and include it in the message that it sends to the destination specified in the target attribute of send.

17. Test 521
If the Processor cannot dispatch the event, it MUST place the error error.communication on the internal event queue of the session that attempted to send the event.

18. Test 553
If the evaluation of send's arguments produces an error, If the evaluation of send's arguments produces an error, the Processor MUST discard the message without attempting to deliver it.

| TOP | Contents | Overview | Examples | Editor | Forum |
|---|